This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I'm Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
In the early days of the pandemic, before we really understood what COVID was, two specialties in the hospital had a foreboding sense that something was very strange about this virus. The first was the pulmonologists, who noticed the striking levels of hypoxemia — low oxygen in the blood — and the rapidity with which patients who had previously been stable would crash in the intensive care unit.
The second, and I mark myself among this group, were the nephrologists. The dialysis machines stopped working right. I remember rounding on patients in the hospital who were on dialysis for kidney failure in the setting of severe COVID infection and seeing clots forming on the dialysis filters. Some patients could barely get in a full treatment because the filters would clog so quickly.
We knew it was worse than flu because of the mortality rates, but these oddities made us realize that it was different too — not just a particularly nasty respiratory virus but one that had effects on the body that we hadn't really seen before.
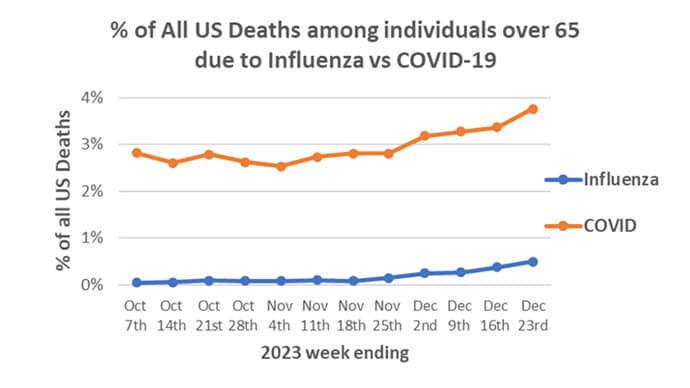
That's why I've always been interested in studies that compare what happens to patients after COVID infection vs what happens to patients after other respiratory infections. This week, we'll look at an intriguing study that suggests that COVID may lead to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and vasculitis.
The study appears in the Annals of Internal Medicine and is made possible by the universal electronic health record systems of South Korea and Japan, who collaborated to create a truly staggering cohort of more than 20 million individuals living in those countries from 2020 to 2021.
The exposure of interest? COVID infection, experienced by just under 5% of that cohort over the study period. (Remember, there was a time when COVID infections were relatively controlled, particularly in some countries.)
The researchers wanted to compare the risk for autoimmune disease among COVID-infected individuals against two control groups. The first control group was the general population. This is interesting but a difficult analysis, because people who become infected with COVID might be very different from the general population. The second control group was people infected with influenza. I like this a lot better; the risk factors for COVID and influenza are quite similar, and the fact that this group was diagnosed with flu means at least that they are getting medical care and are sort of "in the system," so to speak.
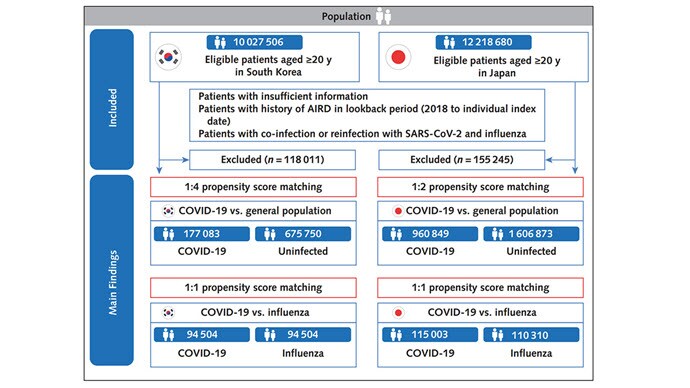
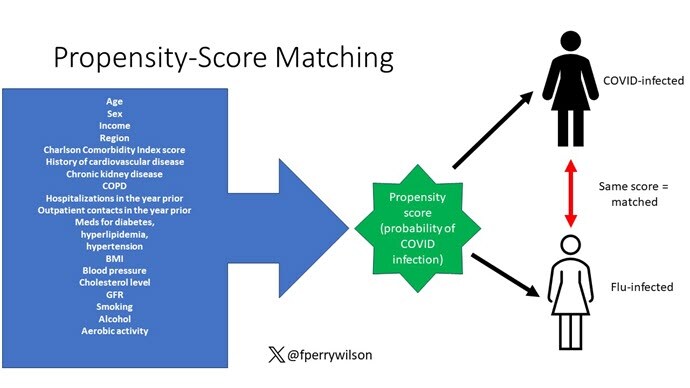
But it's not enough to simply identify these folks and see who ends up with more autoimmune disease. The authors used propensity score matching to pair individuals infected with COVID with individuals from the control groups who were very similar to them. I've talked about this strategy before, but the basic idea is that you build a model predicting the likelihood of infection with COVID, based on a slew of factors — and the slew these authors used is pretty big, as shown below — and then stick people with similar risk for COVID together, with one member of the pair having had COVID and the other having eluded it (at least for the study period).
After this statistical balancing, the authors looked at the risk for a variety of autoimmune diseases.
Compared with those infected with flu, those infected with COVID were more likely to be diagnosed with any autoimmune condition, connective tissue disease, and, in Japan at least, inflammatory arthritis.
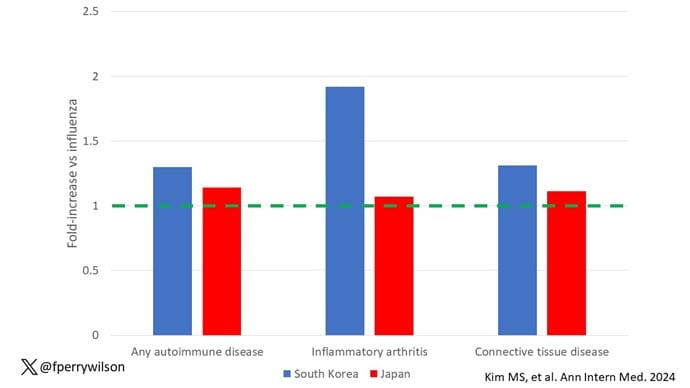
The authors acknowledge that being diagnosed with a disease might not be the same as actually having the disease, so in another analysis they looked only at people who received treatment for the autoimmune conditions, and the signals were even stronger in that group.

This risk seemed to be highest in the 6 months following the COVID infection, which makes sense biologically if we think that the infection is somehow screwing up the immune system.
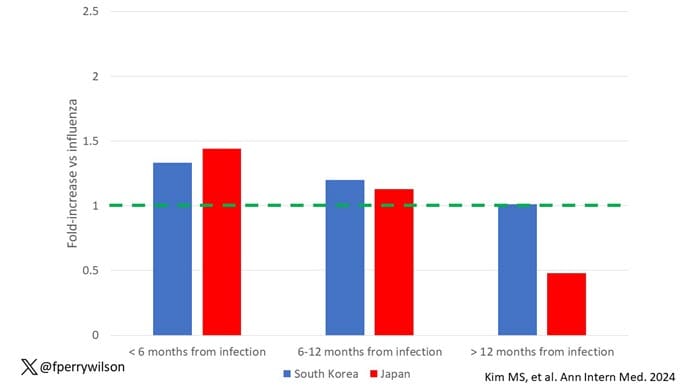
And the risk was similar with both COVID variants circulating at the time of the study.
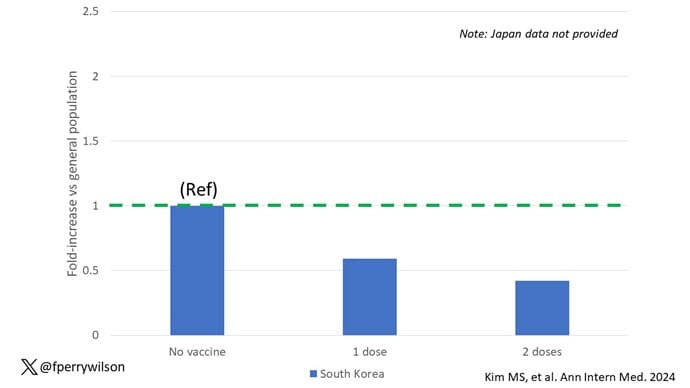
The only factor that reduced the risk? You guessed it: vaccination. This is a particularly interesting finding because the exposure cohort was defined by having been infected with COVID. Therefore, the mechanism of protection is not prevention of infection; it's something else. Perhaps vaccination helps to get the immune system in a state to respond to COVID infection more… appropriately?
Yes, this study is observational. We can't draw causal conclusions here. But it does reinforce my long-held belief that COVID is a weird virus, one with effects that are different from the respiratory viruses we are used to. I can't say for certain whether COVID causes immune system dysfunction that puts someone at risk for autoimmunity — not from this study. But I can say it wouldn't surprise me.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale's Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and here on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and his book, How Medicine Works and When It Doesn't, is available now.